What is the TFCC? TFCC stands for Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex, which is a structure located in the wrist. It plays a crucial role in stabilizing the wrist joint and enabling smooth movements between the ulna (one of the two forearm bones) and the carpal bones in the hand. Injuries to the TFCC can occur due to various reasons, and biomechanical constraints are among the factors that can lead to such injuries.
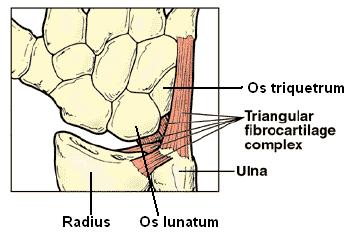
Biomechanical constraints refer to limitations or stresses placed on the body’s tissues, such as ligaments, tendons, and cartilage, during movement or activity. In the case of TFCC injuries, biomechanical constraints can arise from repetitive stress (, sudden impacts, or abnormal loading of the wrist joint. Here are some biomechanical factors that can contribute to TFCC injuries:
- Repetitive motions: Activities that involve repetitive wrist movements, such as in sports (e.g., tennis, golf) or certain occupations (e.g., manual labor, assembly line work), can place prolonged stress on the TFCC. Over time, this repetitive stress can lead to wear and tear on the cartilage and ligaments, increasing the risk of injury.
- Weight-bearing activities: Activities that involve putting significant weight on the hands, such as gymnastics, yoga, or weightlifting, can subject the TFCC to excessive compression forces. This pressure can lead to TFCC injuries, especially if the wrists are not properly supported or aligned during these activities.
- Impact or trauma: Falls or direct blows to the wrist can cause sudden and severe stress on the TFCC, resulting in tears or sprains. Athletes in contact sports or those who engage in activities with a risk of falling are particularly susceptible to this type of injury.
- Poor wrist positioning: Incorrect or awkward wrist positions during various activities, like typing with improper hand and wrist posture, can strain the TFCC and surrounding structures over time.
- Lack of strength and flexibility: Inadequate strength and flexibility in the muscles surrounding the wrist can lead to instability, which may increase the risk of TFCC injuries during physical activities.
To prevent TFCC injuries due to biomechanical constraints, it’s essential to:
- Practice proper ergonomics and wrist positioning during various activities.
- Warm up and stretch before engaging in physical activities involving the wrist.
- Strengthen the muscles in the forearm and wrist through targeted exercises.
- Use protective gear, such as wrist splints or braces, during high-risk activities.
- Take breaks and rest if you engage in repetitive wrist movements for extended periods.
If you suspect a TFCC injury or experience persistent wrist pain or instability, try to find someone well informed on the subject and stay tuned for some home exercises for wrist stability.